NAVSTAR GPS (NAVigation System with Time And Ranging Global Positioning System): is a satellite-based radio system providing 3-D position, navigation and time information to suitable equipped users, at global scale and in any meteorological condition.
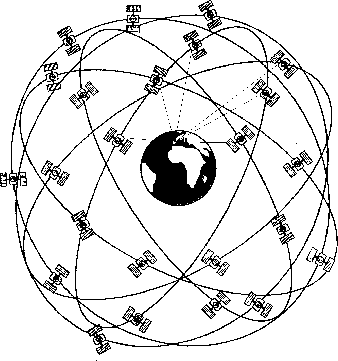
Primarly designed for military purposes (since 1973), GPS consists on
![]() satellites transmitting signals at two L-band frequencies,
at 20,200 km of altitude in circular orbits at 6 different orbital planes
with an inclination of
satellites transmitting signals at two L-band frequencies,
at 20,200 km of altitude in circular orbits at 6 different orbital planes
with an inclination of ![]() degrees and a rotation period of half day:
At least 4 satellites are visible in any time and place...
degrees and a rotation period of half day:
At least 4 satellites are visible in any time and place...
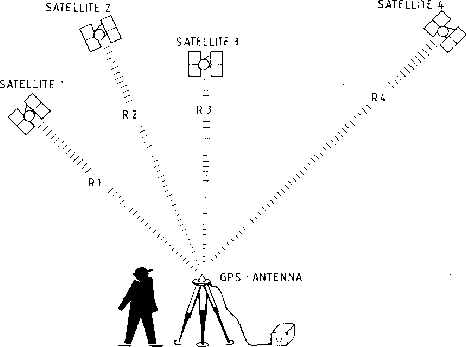
GPS is primarily a navigation system, with this foundation:
The satellite transmits at two L-band frequencies ( ![]() GHz and
GHz and
![]() GHz) pseudorandom codes.
GHz) pseudorandom codes.
This allow to the user "observe" the apparent travel time or delay suffered by the signal between the transmitter j and the receiver (navigation model, other terms neglected):
![]()
Then we need at least 4 observations to solve by Least-Squares the
equation to estimate the receiver 3-D position (x,y,z) and the receiver
clock bias ![]() :
:
![]()
Geometric interpretation: intersection of "spheres"...
The Global Positioning System is usually understood as three segments:
SPACE segment (the satellites)
CONTROL segment (the 5 control stations)
USER segment (the receivers)